1-D finite elements spaces
In this page, we detail the different 1-D finite elements currently implemented in Montjoie. The reference element is the unit interval.
Methods of ElementGeomReference<Dimension>
This class is the base class for 1-D finite elements. We list below the methods of this class.
| Weights | 1-D integration weights |
| Points | 1-D integration points |
| LumpedMassMatrix | returns true if the mass matrix is diagonal |
| GetHybridType | returns 0 |
| GetMemorySize | returns the size used to store the object |
| GetOrder | returns the order of approximation |
| GetGeometryOrder | returns the order of shape functions |
| PointsDof | returns the points associated with degrees of freedom |
| GetNbPointsQuadratureInside | returns the number of integration points |
| GetNbDof | returns the number of degrees of freedom |
| GetNbPointsNodalElt | returns the number of nodal points |
| GetNewNodalInterpolation | returns a finite element projector |
| ConstructFiniteElement | constructs the finite element at a given order |
| GetPolynomialFunctions | returns the basis functions as univariate polynomials |
| ComputeValuesPhiRef | computes the basis functions at a given point of the unit interval |
| ComputeGradientPhiRef | computes the derivative of basis functions at a given point of the unit interval |
| GetValuePhi1D | returns the value of a single 1-D basis function |
| GetGradientPhi1D | returns the derivative of a single 1-D basis function |
| GetValueSinglePhiQuadrature | returns the value of a single basis function on integration points |
| ComputeValuesPhiNodalRef | evaluates the shape functions on a point of the unit interval |
| FjElem | computes Fi(x) for quadrature points |
| FjElemDof | computes Fi(x) for dof points |
| GetStiffnessMatrix | returns the stiffness matrix on the unit interval |
| GetMassMatrix | returns the mass matrix on the unit interval |
| GetGradientMatrix | returns the gradient matrix on the unit interval |
| ComputeIntegralRef | integrates a function against basis functions |
| ApplyCh | integrates a function against basis functions |
| ApplyChTranspose | evaluates a field on integration points |
| ComputeIntegralGradientRef | integrates a function against derivatives of basis functions |
| ComputeProjectionDofRef | projects a function on the finite element basis |
| AddConstantElemMatrix | adds an elementary matrix with constant coefficients |
| AddVariableElemMatrix | adds an elementary matrix with variables coefficients |
EdgeLobatto (inherited from ElementGeomReference)
This class implements 1-D nodal finite element based on Gauss-Lobatto points. The basis functions are given as
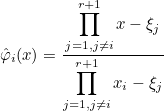
where r is the order of approximation and
 Gauss-Lobatto points on the unit interval. For this class, quadrature points coincide with nodal points leading to a mass lumping. The mass matrix is always diagonal even if the physical index is variable.
Gauss-Lobatto points on the unit interval. For this class, quadrature points coincide with nodal points leading to a mass lumping. The mass matrix is always diagonal even if the physical index is variable.
EdgeGauss (inherited from ElementGeomReference)
The basis functions are the same as for EdgeLobatto. Contrary to EdgeLobatto, integration points no longer coincide with nodal points. Gauss-Legendre points are used for the integration leading to an exact integration of constant elementary matrices. The mass matrix is no longer diagonal.
EdgeHierarchic (inherited from ElementGeomReference)
The basis functions are hierarchical, they are given as
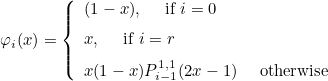
where Pi1, 1 are Jacobi polynomials. These polynomials are orthogonal with respect to the weight function x(1-x). The main advantage of this class is that the elementary matrices (mass, stiffness or gradient) are sparse.
ElementReference<Dimension1, 1>
This class derives from the class ElementReference_Base. It is an interface class that calls the methods of ElementGeomReference. The aim of this class (and derived classes) is to provide a similar structure to 2-D and 3-D finite elements :
- Shape functions (to define geometry) implemented in ElementGeomReference
- Basis functions (to define finite element basis) implemented in ElementReference
- Method GetGeometricElement that returns the geometric element from the finite element class
The classes EdgeLobattoReference, EdgeGaussReference and EdgeHierarchicReference are implementing the same functions as EdgeLobatto, EdgeGauss and EdgeHierarchic, but they derive from ElementReference_Base. Below we show, some example of use of these classes.
// finite element with Gauss-Lobatto points // here we choose a class derived from ElementReference<Dimension1, 1> EdgeLobattoReference edge; // all methods of EdgeLobatto can be used in EdgeLobattoReference edge.ConstructFiniteElement(4); int nb_pts = edge.GetNbPointsQuadratureInside(); // etc // to obtain the class ElementGeomReference, use GetGeometricElement : const ElementGeomReference<Dimension1> elt_geom = edge.GetGeometricElement(); // you can cast this class to EdgeLobatto if you want const EdgeLobatto& edge_geom = static_cast<const EdgeLobatto&>(elt_geom);
Points
Syntax
| VectReal_wp Points |
This attribute stores the integration points of the finite element.
Example :
EdgeLobatto edge; edge.ConstructFiniteElement(4); cout << "Integration points = " << edge.Points << endl;
Location :
FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.hxx
Weights
Syntax
| VectReal_wp Weights |
This attribute stores the integration weights of the finite element.
Example :
EdgeLobatto edge; edge.ConstructFiniteElement(4); cout << "Integration weights = " << edge.Weights << endl;
Location :
FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.hxx
LumpedMassMatrix
Syntax
| bool LumpedMassMatrix() const |
This method returns true if the mass matrix is diagonal (mass lumping).
Example :
EdgeLobatto edge; edge.ConstructFiniteElement(4); bool mass_lumped = edge.LumpedMassMatrix();
Location :
FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.hxx FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReferenceInline.cxx
GetHybridType
Syntax
| int GetHybridType() const |
This method returns 0. It is present to ensure genericity with 2-D finite elements.
Example :
EdgeLobatto edge; edge.ConstructFiniteElement(4); int type = edge.GetHybridType();
Location :
FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.hxx FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReferenceInline.cxx
GetMemorySize
Syntax
| size_t GetMemorySize() const |
This method returns the memory used by the object in bytes.
Example :
EdgeLobatto edge; edge.ConstructFiniteElement(4); size_t mem_used = edge.GetMemorySize();
Location :
FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.hxx FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.cxx
GetOrder
Syntax
| int GetOrder() const |
This method returns the order of approximation for the constructed finite element. It corresponds to the maximal polynomial degree of basis functions.
Example :
EdgeLobatto edge; edge.ConstructFiniteElement(4); int order = edge.GetOrder(); // should give order = 4
Location :
FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.hxx FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReferenceInline.cxx
GetGeometryOrder
Syntax
| int GetGeometryOrder() const |
This method returns the order of approximation for the geometry. It corresponds to the maximal polynomial degree of shape functions.
Example :
EdgeLobatto edge; edge.ConstructFiniteElement(4); int order = edge.GetGeometryOrder(); // should give order = 4
Location :
FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.hxx FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReferenceInline.cxx
PointsDof
Syntax
| const VectReal_wp& PointsDof() const |
This method returns the points associated with degrees of freedom. These points are used to project a function on the finite element basis (with the method ComputeProjectionDofRef).
Example :
EdgeLobatto edge; edge.ConstructFiniteElement(4); const VectReal_wp& pts_dof = edge.PointsDof();
Location :
FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.hxx FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReferenceInline.cxx
GetNbPointsQuadratureInside
Syntax
| int GetNbPointsQuadratureInside() const |
This method returns the number of integration points.
Example :
EdgeLobatto edge; edge.ConstructFiniteElement(4); int nb_pts_quad = edge.GetNbPointsQuadratureInside();
Location :
FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.hxx FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReferenceInline.cxx
GetNbDof
Syntax
| int GetNbDof() const |
This method returns the number of degrees of freedom.
Example :
EdgeLobatto edge; edge.ConstructFiniteElement(4); int nb_dof = edge.GetNbDof();
Location :
FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.hxx FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReferenceInline.cxx
GetNbPointsNodalElt
Syntax
| int GetNbPointsNodalElt() const |
This method returns the number of nodal points.
Example :
EdgeLobatto edge; edge.ConstructFiniteElement(4); int nb_nodes = edge.GetNbPointsNodalElt();
Location :
FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.hxx FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReferenceInline.cxx
GetNewNodalInterpolation
Syntax
| FiniteElementProjector* GetNewNodalInterpolation() const |
This method returns a new projector (class that derives from FiniteElementProjector) that can be used to compute the interpolation from nodal points to other points.
Example :
EdgeLobatto edge; edge.ConstructFiniteElement(4); // we create the object with GetNewNodalInterpolation FiniteElementProjector* proj; proj = edge.GetNewNodalInterpolation(); // then we can compute the projector with Init VectReal_wp other_points(3); other_points(0) = 0.5; other_points(1) = 0.9; other_points(2) = 1.2; proj->Init(edge, other_points); // ProjectScalar to compute the projection of a field from nodal points to the other points VectReal_wp u_nodal(edge.GetNbPointsNodalElt()); u_nodal.FillRand(); VectReal_wp u_other(other_points.GetM()); proj->ProjectScalar(u_nodal, u_other);
Location :
FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.hxx FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReferenceInline.cxx
ConstructFiniteElement
Syntax
| void ConstructFiniteElement(int order, int rgeom, int rquad, int type_quad, int type_func) |
This method constructs a finite element at a given order. Only the first argument is needed, other arguments are optional.
Parameters
- order (in)
- order of approximation for the finite element space
- rgeom (optional)
- order of approximation for shape functions (geometry)
- rquad (optional)
- order for quadrature rules
- type_quad (optional)
- type of integration rule to use
- type_func (optional)
- type of points (for interpolatory finite elements)
Example :
EdgeLobatto edge; edge.ConstructFiniteElement(4);
Location :
FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.hxx FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.cxx
GetPolynomialFunctions
Syntax
| void GetPolynomialFunctions(Vector<UnivariatePolynomial>& phi, Vector<UnivariatePolynomial>& dphi) const |
This method makes explicit the basis functions as polynomials. This method should be used with caution, because the polynomial coefficients can be very large for high order finite elements. The evaluation of these polynomials with Horner algorithm will be instable for very high order. To have stable algorithms, it is advised to call ComputeValuesPhiRef.
Parameters
- phi (out)
- basis functions
- dphi (out)
- derivatives of basis functions
Example :
EdgeLobatto edge; edge.ConstructFiniteElement(4); // if you need to know the polynomial coefficients of the basis functions Vector<UnivariatePolynomial<Real_wp> > phi, dphi; edge.GetPolynomialFunctions(phi, dphi);
Location :
FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.hxx FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.cxx
ComputeValuesPhiRef
Syntax
| void ComputeValuesPhiRef(Real_wp x, VectReal_wp& phi) const |
This method evaluates the basis functions at a given point in the unit interval [0, 1].
Parameters
- x (in)
- coordinate of the point in [0, 1]
- phi (out)
- basis functions evaluated at this point
Example :
EdgeLobatto edge; edge.ConstructFiniteElement(4); // if you need to know phi_i(x) Real_wp x = 0.41; VectReal_wp phi; edge.ComputeValuesPhiRef(x, phi);
Location :
FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.hxx FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.cxx
ComputeGradientPhiRef
Syntax
| void ComputeGradientPhiRef(Real_wp x, VectReal_wp& dphi) const |
This method evaluates the derivative of basis functions at a given point in the unit interval [0, 1].
Parameters
- x (in)
- coordinate of the point in [0, 1]
- dphi (out)
- derivative of basis functions evaluated at this point
Example :
EdgeLobatto edge; edge.ConstructFiniteElement(4); // if you need to know phi_i(x) Real_wp x = 0.41; VectReal_wp phi; edge.ComputeValuesPhiRef(x, phi); // and derivatives VectReal_wp dphi; edge.ComputeGradientPhiRef(x, dphi);
Location :
FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.hxx FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.cxx
GetValuePhi1D
Syntax
| Real_wp GetValuePhi1D(int i, Real_wp x) const |
This method evaluates a single basis function at a given point in the unit interval [0, 1]. Usually, it is more efficient to compute all basis functions (with ComputeValuesPhiRef) than each basis function separately.
Parameters
- i (in)
- basis function number
- x (in)
- coordinate of the point in [0, 1]
Example :
EdgeLobatto edge; edge.ConstructFiniteElement(4); // if you need to evaluate a single basis function phi_i(x) int i = 2; Real_wp x = 0.41; Real_wp phi = edge.GetValuePhi1D(i, x);
Location :
FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.hxx FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.cxx
GetGradientPhi1D
Syntax
| Real_wp GetGradientPhi1D(int i, Real_wp x) const |
This method evaluates the derivative of a single basis function at a given point in the unit interval [0, 1]. Usually, it is more efficient to compute the derivative of all basis functions (with ComputeGradientPhiRef) than each basis function separately.
Parameters
- i (in)
- basis function number
- x (in)
- coordinate of the point in [0, 1]
Example :
EdgeLobatto edge; edge.ConstructFiniteElement(4); // if you need to evaluate a single basis function phi_i(x) int i = 2; Real_wp x = 0.41; Real_wp phi = edge.GetValuePhi1D(i, x); // and its derivative Real_wp dphi = edge.GetGradientPhi1D(i, x);
Location :
FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.hxx FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.cxx
GetValueSinglePhiQuadrature
Syntax
| void GetValueSinglePhiQuadrature(int i, VectReal_wp& phi) const |
This method evaluates a single basis function φi on integration points of the unit interval.
Parameters
- i (in)
- basis function number
- phi (out)
- values of φi on integration points
Example :
EdgeLobatto edge; edge.ConstructFiniteElement(4); // if you need to know phi_i(x_j) where x_j are integration points int i = 2; VectReal_wp phi; edge.GetValueSinglePhiQuadrature(i, phi);
Location :
FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.hxx FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.cxx
ComputeValuesPhiNodalRef
Syntax
| void ComputeValuesPhiNodalRef(Real_wp x, VectReal_wp& phi) const |
This method evaluates the shape functions at a given point in the unit interval [0, 1].
Parameters
- x (in)
- coordinate of the point in [0, 1]
- phi (out)
- shape functions evaluated at this point
Example :
EdgeLobatto edge; edge.ConstructFiniteElement(4); // if you need to know phi_i(x) where phi_i are Lagrange polynomial associated with nodal points Real_wp x = 0.41; VectReal_wp phi; edge.ComputeValuesPhiNodalRef(x, phi);
Location :
FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.hxx FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.cxx
FjElem
Syntax
| void FjElem(const VectReal_wp& s, VectReal_wp& points) const |
This method computes the integration points on the real interval [s0, s1]:
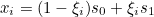
where
 are integration points on the unit interval [0, 1].
are integration points on the unit interval [0, 1].
Parameters
- s (in)
- extremities of the real interval
- points (out)
- integration points on the real interval
Example :
EdgeLobatto edge; edge.ConstructFiniteElement(4); // extremities of the element VectReal_wp s(2); s(0) = 3.0; s(1) = 3.2; // integration points on the real interval VectReal_wp points; edge.FjElem(s, points);
Location :
FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.hxx FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.cxx
FjElemDof
Syntax
| void FjElemDof(const VectReal_wp& s, VectReal_wp& points) const |
This method computes the dof points on the real interval [s0, s1]:
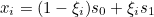
where
 are dof points on the unit interval [0, 1].
are dof points on the unit interval [0, 1].
Parameters
- s (in)
- extremities of the real interval
- points (out)
- dof points on the real interval
Example :
EdgeLobatto edge; edge.ConstructFiniteElement(4); // extremities of the element VectReal_wp s(2); s(0) = 3.0; s(1) = 3.2; // dof points on the real interval VectReal_wp points; edge.FjElemDof(s, points);
Location :
FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.hxx FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.cxx
GetStiffnessMatrix
Syntax
| const Matrix<Real_wp, Symmetric, RowSymPacked>& GetStiffnessMatrix() const |
This method returns the stiffness matrix given as:
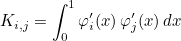
where φi are basis functions. The stiffness matrix is returned as a dense matrix even though it may be sparse.
Example :
EdgeLobatto edge; edge.ConstructFiniteElement(4); // stiffness matrix const Matrix<Real_wp, Symmetric, RowSymPacked>& K = edge.GetStiffnessMatrix();
Location :
FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.hxx FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReferenceInline.cxx
GetMassMatrix
Syntax
| const Matrix<Real_wp, Symmetric, RowSymPacked>& GetMassMatrix() const |
This method returns the mass matrix given as:
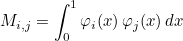
where φi are basis functions. The mass matrix is returned as a dense matrix even though it may be sparse.
Example :
EdgeLobatto edge; edge.ConstructFiniteElement(4); // mass matrix const Matrix<Real_wp, Symmetric, RowSymPacked>& M = edge.GetMassMatrix();
Location :
FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.hxx FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReferenceInline.cxx
GetGradientMatrix
Syntax
| const Matrix<Real_wp>& GetGradientMatrix() const |
This method returns the gradient matrix given as:
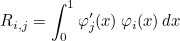
where φi are basis functions. The gradient matrix is returned as a dense matrix even though it may be sparse.
Example :
EdgeLobatto edge; edge.ConstructFiniteElement(4); // gradient matrix const Matrix<Real_wp>& R = edge.GetGradientMatrix();
Location :
FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.hxx FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReferenceInline.cxx
ComputeIntegralRef
Syntax
| void ComputeIntegralRef(const Vector& feval, Vector& res) const |
This method computes the integral of a function against basis functions :

where φi are basis functions. Contrary to 2-D or 3-D finite elements, the input vector contains evaluations of the function f without multiplication by integration weights.
Parameters
- feval (in)
- values of f on integration points
- res (out)
- result vector
Example :
EdgeLobatto edge;
edge.ConstructFiniteElement(4);
// number of integration points
int nb_pts = edge.GetNbPointsQuadratureInside();
// we evaluate a function f = cos(x)
VectReal_wp feval(nb_pts);
for (int i = 0; i < nb_pts; i++)
feval(i) = cos(edge.Points(i));
// integration against basis functions
VectReal_wp contrib;
edge.ComputeIntegralRef(feval, contrib);
Location :
FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.hxx FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.cxx
ApplyCh
Syntax
| void ApplyCh(const Vector& feval, Vector& res) const |
This method computes the integral of a function against basis functions :
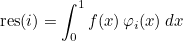
where φi are basis functions. Contrary to ComputeIntegralRef, the input vector contains evaluations of the function f multiplied by integration weights. Since weights are included, the result is given as
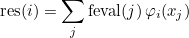
where xj are integration points.
Parameters
- feval (in)
- values of f on integration points (multiplied by weights)
- res (out)
- result vector
Example :
EdgeLobatto edge;
edge.ConstructFiniteElement(4);
// number of integration points
int nb_pts = edge.GetNbPointsQuadratureInside();
// we evaluate a function f = cos(x) and we multiply with the weights
VectReal_wp feval(nb_pts);
for (int i = 0; i < nb_pts; i++)
feval(i) = edge.Weights(i)*cos(edge.Points(i));
// integration against basis functions
VectReal_wp contrib;
edge.ApplyCh(feval, contrib);
Location :
FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.hxx FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.cxx
ApplyChTranspose
Syntax
| void ApplyChTranspose(const Vector& u, Vector& u_quad) const |
This method evaluates a field on integration points from components on degrees of freedom. The result is given as :
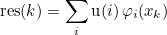
where φi are basis functions and xk integration points.
Parameters
- u (in)
- components on degrees of freedom
- res (out)
- values on integration points
Example :
EdgeLobatto edge; edge.ConstructFiniteElement(4); // starting from a field defined on degrees of freedom VectReal_wp u(edge.GetNbDof()); u.FillRand(); // values of u on integration points VectReal_wp u_quad; edge.ApplyChTranspose(u, u_quad);
Location :
FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.hxx FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.cxx
ComputeIntegralGradientRef
Syntax
| void ComputeIntegralGradientRef(const Vector& feval, Vector& res) const |
This method computes the integral of a function against the derivative of basis functions :
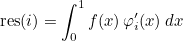
where φi are basis functions. Contrary to 2-D or 3-D finite elements, the input vector contains evaluations of the function f without multiplication by integration weights.
Parameters
- feval (in)
- values of f on integration points
- res (out)
- result vector
Example :
EdgeLobatto edge;
edge.ConstructFiniteElement(4);
// number of integration points
int nb_pts = edge.GetNbPointsQuadratureInside();
// we evaluate a function f = cos(x)
VectReal_wp feval(nb_pts);
for (int i = 0; i < nb_pts; i++)
feval(i) = cos(edge.Points(i));
// integration against the derivative of basis functions
VectReal_wp contrib;
edge.ComputeIntegralGradientRef(feval, contrib);
Location :
FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.hxx FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.cxx
ComputeProjectionDofRef
Syntax
| void ComputeProjectionDofRef(const Vector& feval, Vector& res) const |
This method projects a field f on the finite element basis. The input vector feval contains the evaluation of f on dof points.
Parameters
- feval (in)
- values of f on dof points
- res (out)
- result vector
Example :
EdgeLobatto edge;
edge.ConstructFiniteElement(4);
// number of dof points
int nb_pts = edge.PointsDof().GetM();
// we evaluate a function f = cos(x)
VectReal_wp feval(nb_pts);
for (int i = 0; i < nb_pts; i++)
feval(i) = cos(edge.PointsDof()(i));
// projection on degrees of freedom
VectReal_wp u;
edge.ComputeProjectionDofRef(feval, u);
Location :
FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.hxx FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.cxx
AddConstantElemMatrix
Syntax
| void AddConstantElemMatrix(int m, int n, Real_wp mass, Real_wp C, Real_wp D, Real_wp E, TinyVector<bool, 4> null_term, VirtualMatrix& A) const |
This method adds an elementary matrix to the matrix A :
A[m:m+N, n:n+N] += B
where N is the number of degrees of freedom. The elementary matrix B is given as

where mass, C, D and E are constant coefficients and φi are basis functions. mass C, D and E are constant coefficients. For example if you have the following matrix in the real interval [a, b]:
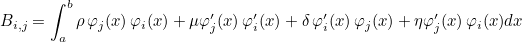
where ρ, μ, δ and η are constant physical indexes. This integral is transformed in the unit interval :
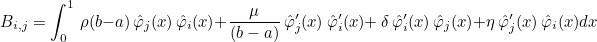
Therefore, you can set the coefficients mass, C, D and E with :
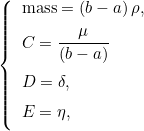
Then you can call the method AddConstantElemMatrix. The destination matrix A derives from the class VirtualMatrix, it can be a symmetric or general matrix (even sparse). The argument null_term can be used if you want to skip some terms. If null_term(0) is true, the term with mass is not computed (nor added). If null_term(1) is true, the term with C is not computed. If null_term(2) (resp. null_term(3)) is true, the term with D (resp. E) is not computed.
Parameters
- m (in)
- starting row index for A
- n (in)
- starting column index for A
- mass (in)
- coefficient mass
- C (in)
- coefficient C
- D (in)
- coefficient D
- E (in)
- coefficient E
- null_term (in)
- if null_term(i) the i-th term is not computed
- A (inout)
- matrix to which the mass matrix will be added
Example :
EdgeLobatto edge; edge.ConstructFiniteElement(4); // given interval Real_wp a = 2.0, b = 2.5; // physical indexes Real_wp rho = 2.0, mu = 3.0, delta = 0.8, eta = 1.4; // taking into account transformation into the unit interval Real_wp mass = rho*(b-a), C = mu/(b-a), D = delta, E = eta; // we compute the elementary matrix int N = edge.GetNbDof(); Matrix<Real_wp, Symmetric, RowSymPacked> A(N, N); A.Zero(); TinyVector<bool, 4> null_term(false, false, false, false); edge.AddConstantElemMatrix(0, 0, mass, C, D, E, null_term, A);
Location :
FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.hxx FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.cxx
AddVariableElemMatrix
Syntax
| void AddVariableElemMatrix(int m, int n, Real_wp mass, Real_wp C, Real_wp D, Real_wp E, TinyVector<bool, 4> null_term, VirtualMatrix& A) const |
This method adds an elementary matrix to the matrix A :
A[m:m+N, n:n+N] += B
where N is the number of degrees of freedom. The elementary matrix B is given as
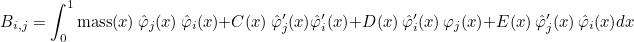
where mass, C, D and E are variable coefficients and φi are basis functions. For example if you have the following matrix in the real interval [a, b]:
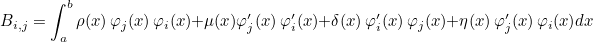
where ρ, μ, δ and η are physical indexes. This integral is transformed in the unit interval :
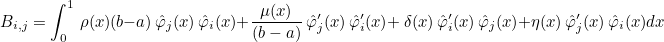
Therefore, you can set the coefficients mass, C, D and E with :
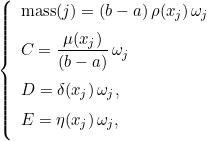
where xj, ωj are quadrature points and weights. Then you can call the method AddVariableElemMatrix. The destination matrix A derives from the class VirtualMatrix, it can be a symmetric or general matrix (even sparse). Since the weights are already included in the coefficients, the method performs the following operation:
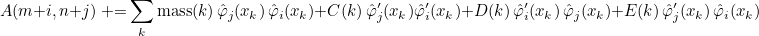
The argument null_term can be used if you want to skip some terms. If null_term(0) is true, the term with mass is not computed (nor added). If null_term(1) is true, the term with C is not computed. If null_term(2) (resp. null_term(3)) is true, the term with D (resp. E) is not computed.
Parameters
- m (in)
- starting row index for A
- n (in)
- starting column index for A
- mass (in)
- coefficient mass
- C (in)
- coefficient C
- D (in)
- coefficient D
- E (in)
- coefficient E
- null_term (in)
- if null_term(i) the i-th term is not computed
- A (inout)
- matrix to which the mass matrix will be added
Example :
EdgeLobatto edge;
edge.ConstructFiniteElement(4);
// number of quadrature points
int nb_pts = edge.NbPointsQuadratureInside();
// given interval
Real_wp a = 2.0, b = 2.5;
// physical indexes (to be evaluated on integration points)
VectReal_wp rho(nb_pts), mu(nb_pts), delta(nb_pts), eta(nb_pts);
rho.FillRand(); mu.FillRand(); delta.FillRand(); eta.FillRand();
// taking into account transformation into the unit interval
VectReal_wp mass(nb_pts), C(nb_pts), D(nb_pts), E(nb_pts);
for (int i = 0; i < nb_pts; i++)
{
mass(i) = rho(i)*(b-a)*edge.Weights(i);
C(i) = mu(i)/(b-a)*edge.Weights(i);
D(i) = delta(i)*edge.Weights(i); E(i) = eta(i)*edge.Weights(i);
}
// we compute the elementary matrix
int N = edge.GetNbDof();
Matrix<Real_wp, Symmetric, RowSymPacked> A(N, N);
A.Zero();
TinyVector<bool, 4> null_term(false, false, false, false);
edge.AddVariableElemMatrix(0, 0, mass, C, D, E, null_term, A);
Location :
FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.hxx FiniteElement/Edge/EdgeReference.cxx